HSE Scientists Reveal How Disrupted Brain Connectivity Affects Cognitive and Social Behaviour in Children with Autism

An international team of scientists, including researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, has for the first time studied the connectivity between the brain's sensorimotor and cognitive control networks in children with autism. Using fMRI data, the researchers found that connections within the cognitive control network (responsible for attention and inhibitory control) are weakened, while connections between this network and the sensorimotor network (responsible for movement and sensory processing) are, by contrast, excessively strong. These features manifest as difficulties in social interaction and behavioural regulation in children. The study has been published in Brain Imaging and Behavior.
For a person to focus attention, move, perceive others, and regulate their own behaviour at the same time, the brain engages multiple functional networks. Each network is responsible for a specific function: attention, movement, perception, or behavioural regulation. As individuals mature, the internal connections within these networks strengthen, while the connections between different networks, by contrast, tend to weaken. This allows the brain to allocate responsibilities across its systems, so they can operate independently without interfering with one another. This process is known as network segregation.
However, in autism spectrum disorders (ASD), network segregation may be disrupted. Autism spectrum disorders are neurodevelopmental conditions that alter the way individuals perceive information, interact with others, and respond to the world around them. To understand how disruptions in brain networks relate to these changes, researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, the Institute of Linguistics of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and the Seattle Children’s Research Institute studied, for the first time, the interaction between two key networks: the cognitive control network—responsible for attention, inhibitory control, and planning—and the sensorimotor network, which is involved in movement and sensory information processing.
The researchers analysed fMRI data from 121 children with ASD and 84 typically developing children, aged 5 to 14, and also administered four behavioural questionnaires to assess how the children interact with others, regulate their thoughts and actions, shift attention, and control their movements.
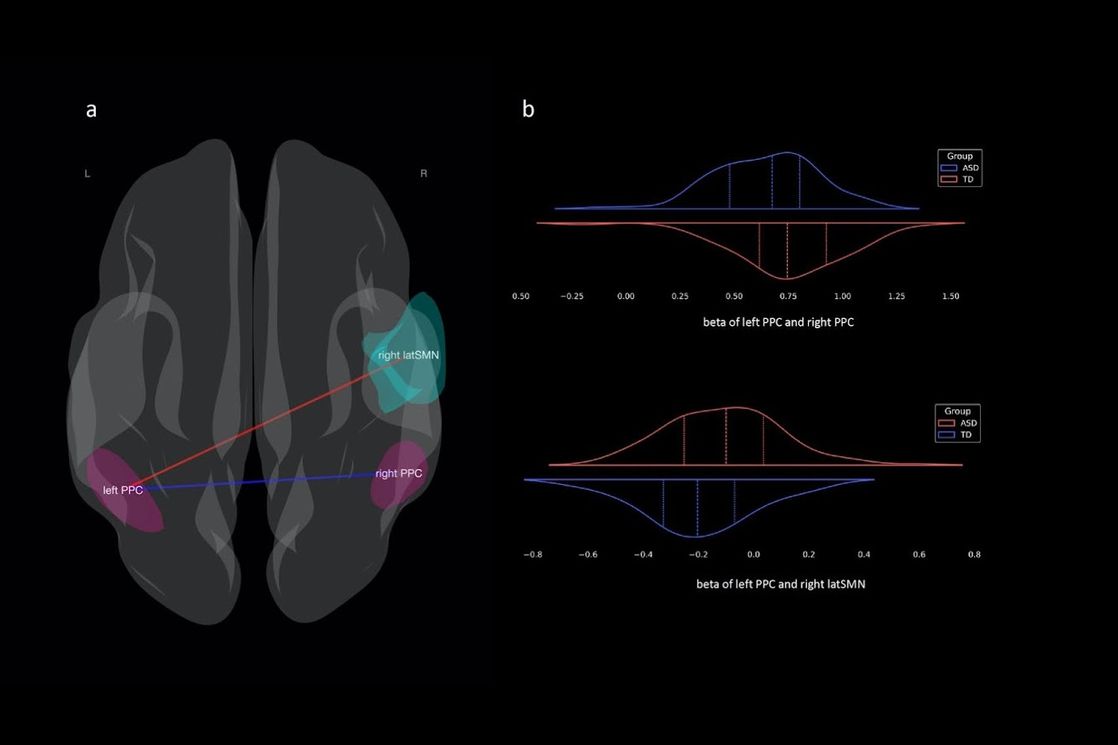
The study found that children with ASD have significantly weaker connections within the cognitive control network. The weaker the connections, the greater the difficulty the child experienced in regulating behaviour and shifting attention—findings that were also confirmed by the behavioural test results.
At the same time, the connections between the cognitive control network and the sensorimotor network were found to be excessively strong. This characteristic was associated with difficulties in social interaction and behaviour. However, neither stronger nor weaker connectivity affected the child’s ability to control their movements.

Alina Minnigulova
'In children with autism, the balance between autonomous functioning of networks and their interaction is disrupted. Rather than smooth internal coordination, excessive cross-activity occurs, hindering the brain’s ability to adapt when switching between external and internal signals,' explains Alina Minnigulova, Research Fellow at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain.
Importantly, these deviations are not only observable on fMRI but also correlate with specific manifestations of the disorder, such as communication difficulties, attention deficits, and problems with planning and task switching. These findings will advance our understanding of the neurophysiological mechanisms underlying ASD and may, in the future, support faster diagnosis of these conditions.
See also:
Scientists Test Asymmetry Between Matter and Antimatter
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has collected and analysed data from dozens of experiments on charm mixing—the process in which an unstable charm meson oscillates between its particle and antiparticle states. These oscillations were observed only four times per thousand decays, fully consistent with the predictions of the Standard Model. This indicates that no signs of new physics have yet been detected in these processes, and if unknown particles do exist, they are likely too heavy to be observed with current equipment. The paper has been published in Physical Review D.
HSE Scientists Reveal What Drives Public Trust in Science
Researchers at HSE ISSEK have analysed the level of trust in scientific knowledge in Russian society and the factors shaping attitudes and perceptions. It was found that trust in science depends more on everyday experience, social expectations, and the perceived promises of science than on objective knowledge. The article has been published in Universe of Russia.
Institute for Robotics Systems Established at HSE University
As decided by the HSE University Academic Council, a new Institute for Robotics Systems will be established at HSE, and with a strong fundamental base. It will cooperate with relevant departments across the university and engage students and doctoral candidates in research and development (R&D). First Vice Rector of HSE University and Director of the Institute for Statistical Studies and Economics of Knowledge, Leonid Gokhberg, discussed the expected practical results and the framework for cooperation with an industrial partner.
Scientists Uncover Why Consumers Are Reluctant to Pay for Sugar-Free Products
Researchers at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have investigated how 'sugar-free' labelling affects consumers’ willingness to pay for such products. It was found that the label has little impact on the products’ appeal due to a trade-off between sweetness and healthiness: on the one hand, the label can deter consumers by implying an inferior taste, while on the other, it signals potential health benefits. The study findings have been published in Frontiers in Nutrition.
HSE Tops Ranking of Universities Participating in Priority 2030 Programme
The Russian Ministry of Science and Higher Education has published an updated list of participants in the Priority 2030 programme. A total of 106 universities will receive support this year. HSE University was included in the first group and topped the ranking.
HSE Psycholinguists Launch Digital Tool to Spot Dyslexia in Children
Specialists from HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain have introduced LexiMetr, a new digital tool for diagnosing dyslexia in primary school students. This is the first standardised application in Russia that enables fast and reliable assessment of children’s reading skills to identify dyslexia or the risk of developing it. The application is available on the RuStore platform and runs on Android tablets.
HSE Scientists Optimise Training of Generative Flow Networks
Researchers at the HSE Faculty of Computer Science have optimised the training method for generative flow neural networks to handle unstructured tasks, which could make the search for new drugs more efficient. The results of their work were presented at ICLR 2025, one of the world’s leading conferences on machine learning. The paper is available at Arxiv.org.
Physicists Propose New Mechanism to Enhance Superconductivity with 'Quantum Glue'
A team of researchers, including scientists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that defects in a material can enhance, rather than hinder, superconductivity. This occurs through interaction between defective and cleaner regions, which creates a 'quantum glue'—a uniform component that binds distinct superconducting regions into a single network. Calculations confirm that this mechanism could aid in developing superconductors that operate at higher temperatures. The study has been published in Communications Physics.
Neural Network Trained to Predict Crises in Russian Stock Market
Economists from HSE University have developed a neural network model that can predict the onset of a short-term stock market crisis with over 83% accuracy, one day in advance. The model performs well even on complex, imbalanced data and incorporates not only economic indicators but also investor sentiment. The paper by Tamara Teplova, Maksim Fayzulin, and Aleksei Kurkin from the Centre for Financial Research and Data Analytics at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences has been published in Socio-Economic Planning Sciences.
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.