.jpg)
Solvent Instead of Toxic Reagents: Chemists Develop Environmentally Friendly Method for Synthesising Aniline Derivatives
An international team of researchers, including chemists from HSE University and the A.N. Nesmeyanov Institute of Organoelement Compounds of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INEOS RAS), has developed a new method for synthesising aniline derivatives—compounds widely used in the production of medicines, dyes, and electronic materials. Instead of relying on toxic and expensive reagents, they proposed using tetrahydrofuran, which can be derived from renewable raw materials. The reaction was carried out in the presence of readily available cobalt salts and syngas. This approach reduces hazardous waste and simplifies the production process, making it more environmentally friendly. The study has been published in ChemSusChem.

Scientists Have Modelled Supercapacitor Operation at Molecular and Ionic Level
HSE scientists used supercomputer simulations to study the behaviour of ions and water molecules inside the nanopores of a supercapacitor. The results showed that even a very small amount of water alters the charge distribution inside the nanopores and influences the device’s energy storage capacity. This approach makes it possible to predict how supercapacitors behave under different electrolyte compositions and humidity conditions. The paper has been published in Electrochimica Acta. The study was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (RSF).
.jpg)
Cerium Glows Yellow: Chemists Discover How to Control Luminescence of Rare Earth Elements
Researchers at HSE University and the Institute of Petrochemical Synthesis of the Russian Academy of Sciences have discovered a way to control both the colour and brightness of the glow emitted by rare earth elements. Their luminescence is generally predictable—for example, cerium typically emits light in the ultraviolet range. However, the scientists have demonstrated that this can be altered. They created a chemical environment in which a cerium ion began to emit a yellow glow. The findings could contribute to the development of new light sources, displays, and lasers. The study has been published in Optical Materials.
%20%D0%B1%D0%B5%D0%B7%20%D0%BE%D1%87%D0%B8%D1%81%D1%82%D0%BA%D0%B8%20%E2%80%94%20%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BF%D0%B8%D1%8F.jpg)
Chemists Simplify Synthesis of Drugs Involving Amide Groups
Chemists from HSE University and the Nesmeyanov Institute of Organoelement Compounds of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INEOS RAS) have developed a new method for synthesising amides, essential compounds in drug production. Using a ruthenium catalyst and carbon monoxide under precisely controlled reaction conditions, they successfully obtained the target product without by-products or complex purification steps. The method has already been tested for synthesising a key component of Vorinostat, a drug used to treat T-cell lymphoma. This approach could lower the cost of the drug by orders of magnitude. The paper has been published in the Journal of Catalysis. The study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation.

Russian Scientists Develop New Compound for Treating Aggressive Tumours
A team of Russian researchers has synthesised a novel compound for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT), a treatment for advanced cancer that uses the boron-10 isotope. The compound exhibits low toxicity, excellent water solubility, and eliminates the need for administering large volumes. Most importantly, the active substance reaches the tumour with minimal impact on healthy tissues. The study was published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences shortly before World Cancer Day, observed annually on February 4.

Russian Scientists Improve Water Purification Membranes Using Metal Ions
Researchers have proposed using polymer membranes modified with copper, zinc, and chromium metal ions for water purification. These polymers were used for the first time in water purification via electrodialysis. Copper-based membranes demonstrated record selectivity for monovalent ions, opening new possibilities for sustainable water recycling. The study has been published in the Journal of Membrane Science.
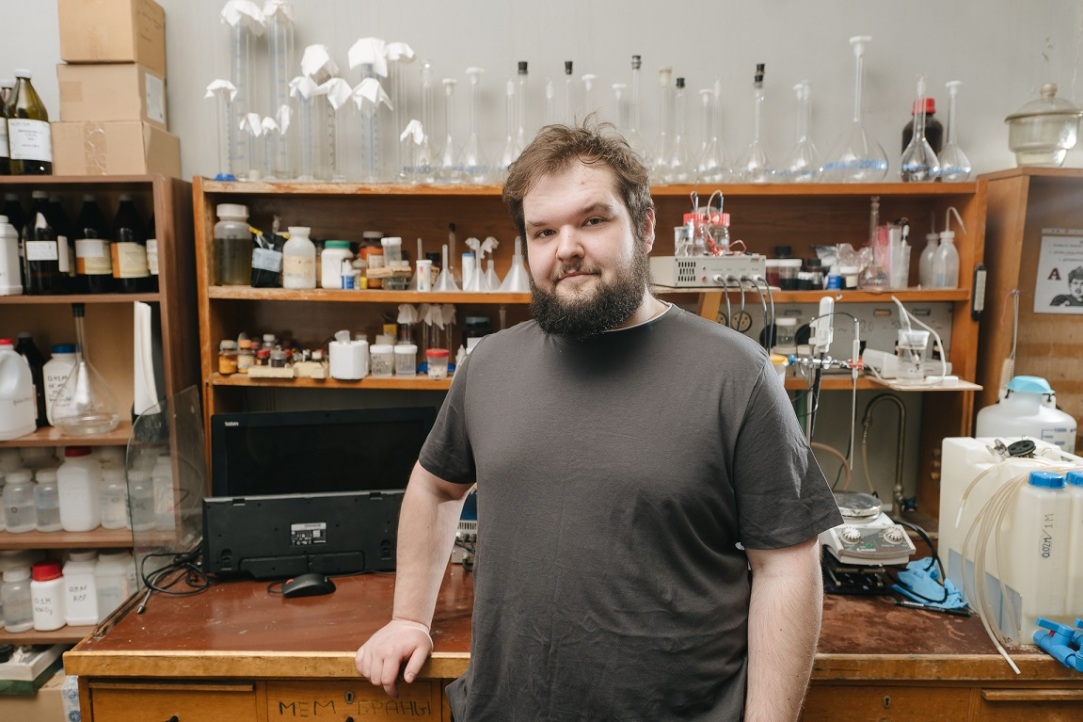

'I Would Ask Mendeleev if It's True that He Invented Vodka'
Andrey Manin's research focuses on membranes, but he has not yet decided whether to dedicate his PhD thesis to those used in water desalination or those involved in new types of electricity generation. In this interview with the HSE Young Scientists project, he recalls how he once disliked organic chemistry, enjoys watching retro films at Illusion Cinema, and was fascinated by Red Square as a child.

HSE Faculty of Chemistry Professor Wins Vyzov Prize
On December 9, 2024, the winners of the Vyzov Prize for Future Technologies were announced. Professor Leonid Fershtat from the Joint Department of Organic Chemistry with the RAS Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry was honoured in the ‘Future’ category for his advanced research on creating functional organic materials for multi-purpose use based on high-nitrogen molecular architectures.

Ruthenium Complexes Can Accelerate the Development of New Medicines
A group of scientists at INEOS RAS, HSE University, and MIPT have synthesised catalysts containing a ruthenium atom and an aromatic ring. The scientists have isolated the mirror forms of these catalysts and investigated their effectiveness in producing heterocycles, which are commonly found in the structures of drugs. The research findings have been published in Chemical Communications.
Russian Chemists Develop Luminous Pseudosandwich Composed of Rare Earth Metals
A team of Russian researchers has successfully synthesised a new class of complex compounds of rare earth elements. Unlike other lanthanide compounds, the resulting substances are highly soluble in most organic solvents. These novel compounds can find application in organic and organometallic synthesis, as well as in the production of new luminescent materials. The study has been published in Inorganic Chemistry.